In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, site speed is paramount to online success. A slow-loading website can significantly impact your conversion rates, leading to lost revenue and frustrated users. This article will delve into proven strategies to supercharge your conversions by optimizing your site speed. We’ll explore practical tips and techniques that you can implement to enhance user experience and ultimately, boost your bottom line. Understanding the importance of site speed is the first step towards achieving optimal performance and maximizing your online potential.
From optimizing images and leveraging browser caching to minimizing HTTP requests and choosing the right hosting provider, we’ll cover a range of actionable steps to improve your site speed. Learn how to identify bottlenecks and implement effective solutions to supercharge your conversions. By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how site speed impacts your business and possess the knowledge to transform your website into a high-performing conversion machine.
Understanding the Impact of Site Speed on Conversions
In today’s fast-paced digital world, site speed plays a critical role in online success. A slow-loading website can significantly impact your conversion rates, leading to lost revenue and frustrated users.
Studies have shown a strong correlation between site speed and conversion rates. Even a one-second delay in page load time can result in a noticeable drop in conversions. Users expect websites to load quickly, and if they encounter delays, they are more likely to abandon their carts or leave without completing desired actions.
Slow loading times contribute to a poor user experience, increasing bounce rates and negatively affecting search engine rankings. Search engines prioritize websites that provide a seamless and efficient user experience, and site speed is a key factor in this assessment.
By optimizing your site speed, you can improve user satisfaction, increase engagement, and ultimately boost your bottom line. A faster website leads to a more positive user experience, encouraging visitors to explore more pages, spend more time on your site, and ultimately convert into paying customers.
Analyzing Your Current Site Speed Performance
Before implementing any optimization strategies, it’s crucial to understand your website’s current performance. This baseline measurement will allow you to track progress and identify the most impactful changes.
Several tools can help analyze your site speed. Google PageSpeed Insights provides valuable data and recommendations. GTmetrix offers a detailed performance report with actionable insights. WebPageTest allows you to test from various locations and browsers, simulating real-world user experiences.
These tools typically offer metrics like First Contentful Paint (FCP), Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), and Time to Interactive (TTI). Understanding these metrics will pinpoint specific areas for improvement.
Pay close attention to identified bottlenecks. These might include large image files, unoptimized code, or inefficient server responses. Prioritize addressing the issues with the greatest potential impact on performance.
Optimizing Images for Web Performance
Images are often the largest contributors to page bloat, hindering site speed and impacting conversions. Optimizing them is crucial for a fast-loading website. Choosing the right image format is the first step.
Use WebP whenever possible. This modern format offers superior compression and quality compared to older formats like JPEG and PNG. If WebP isn’t supported by all your target browsers, consider serving JPEG or PNG as a fallback.
Compress your images regardless of the format. Tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim can significantly reduce file sizes without noticeable quality loss. Resize images to the dimensions they’re displayed on your site. Don’t upload a 2000px wide image if it’s only displayed at 500px.
Consider using lazy loading, a technique that defers loading of images until they’re visible in the viewport. This reduces initial page load time and improves the user experience, especially on pages with numerous images.
Leveraging Browser Caching Effectively
Browser caching is a powerful technique to significantly improve website speed. It allows a visitor’s browser to store static assets, such as images, CSS files, and JavaScript files, locally on their computer. When a user revisits your site, the browser can load these assets from the local cache instead of re-downloading them from the server, resulting in faster page load times.
You can control how long these assets are stored locally by configuring the appropriate HTTP headers. These headers, like Cache-Control and Expires, instruct the browser on how long to keep a resource in its cache before requesting a fresh copy from the server. A longer cache lifespan can drastically reduce the amount of data that needs to be transferred on subsequent visits.
Properly configuring browser caching can drastically reduce HTTP requests, decrease server load, and provide a more responsive browsing experience for your visitors. This ultimately leads to improved user satisfaction and higher conversion rates.
Minifying CSS and JavaScript Files
Minification is the process of removing unnecessary characters from your CSS and JavaScript files without changing their functionality. This reduces file size, leading to faster download times and improved page load speed.
Whitespace, comments, and long variable names, while helpful for development, contribute to larger file sizes. Minification eliminates these extra elements, creating a more compact version of your code that browsers can parse more quickly. This seemingly small optimization can have a significant impact on overall site performance.
There are numerous tools available to minify your files, both online and offline. Many build tools and code editors offer built-in minification features or plugins. Choose a method that fits your workflow and ensures seamless integration with your development process.
By minifying your CSS and JavaScript files, you streamline the delivery of your website’s styling and interactive elements, directly contributing to a faster, more efficient user experience.
Choosing the Right Hosting Provider for Your Needs

Your hosting provider plays a critical role in website speed. Choosing the wrong provider can significantly hinder performance and impact conversions. Different hosting options cater to varying needs and website sizes.
For smaller websites or blogs, shared hosting can be a cost-effective starting point. However, as your site grows, consider upgrading to a more robust solution. VPS (Virtual Private Server) hosting offers more dedicated resources and improved performance compared to shared hosting.
Dedicated servers provide the highest level of control and performance, allocating an entire server solely to your website. This is ideal for high-traffic websites with demanding resource requirements. For websites built with specific technologies, specialized hosting like cloud or WordPress hosting may be more suitable.
When evaluating hosting providers, consider factors like server location, uptime guarantees, and customer support. Choosing a provider with servers closer to your target audience can significantly reduce latency. A strong uptime guarantee ensures your site remains accessible, maximizing potential conversions. Finally, reliable customer support can assist you with any technical issues that may arise, minimizing downtime.
Implementing a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a geographically distributed network of servers that work together to deliver web content faster. By caching static assets like images, CSS, and JavaScript files on servers closer to your users, a CDN significantly reduces latency. This results in a faster loading experience, regardless of where your visitors are located.
Reduced latency translates to improved user experience and higher conversion rates. When users don’t have to wait for a page to load, they’re more likely to engage with your content and complete desired actions, such as making a purchase or filling out a form. CDNs also help handle traffic spikes, ensuring your site remains accessible even during periods of high demand.
Choosing the right CDN is crucial. Consider factors like your target audience’s geographical distribution, the CDN’s performance, and its pricing structure. Many reputable CDN providers offer varying levels of service to suit different needs and budgets.
Mobile Optimization: Catering to On-the-Go Shoppers
In today’s mobile-first world, optimizing your website for mobile devices is no longer optional—it’s essential. A slow mobile experience can lead to frustrated users and lost conversions. Prioritize a mobile-responsive design that adapts seamlessly to various screen sizes.
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) is a powerful technology that creates lightweight versions of your web pages, dramatically improving load times on mobile devices. Consider implementing AMP to enhance the mobile user experience.
Minimize HTTP requests on mobile by combining files and leveraging browser caching. Every additional request adds latency, especially on mobile networks where connectivity can be inconsistent.
Optimize images specifically for mobile consumption. Use appropriate image formats (like WebP) and compress images to reduce file sizes without sacrificing quality. This will significantly improve mobile page load speed.
Monitoring and Continuously Improving Site Speed
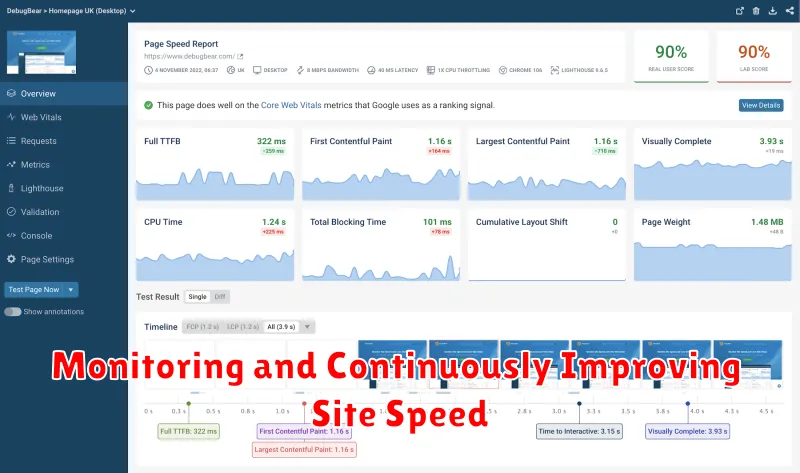
Regular monitoring is crucial for maintaining optimal site speed. Utilize tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and GTmetrix to track performance metrics and identify areas for improvement. These tools provide detailed reports, highlighting specific issues impacting load times.
Establish a baseline performance score and track changes over time. This allows you to identify the impact of any modifications made to the website. Set up alerts to notify you of any significant drops in performance, allowing for prompt intervention and remediation.
Continuous improvement involves regularly reviewing and optimizing website elements. Implement A/B testing to assess the impact of changes on both site speed and conversion rates. Continuously analyze performance data to identify potential bottlenecks and prioritize optimization efforts.

