In today’s competitive e-commerce landscape, dynamic pricing has emerged as a powerful tool for businesses aiming to optimize revenue and stay ahead of the curve. This sophisticated strategy involves adjusting product prices in real-time, responding to fluctuations in demand, competitor pricing, and market conditions. Mastering dynamic pricing can unlock significant advantages, from maximizing profits during peak seasons to maintaining competitiveness during periods of low demand. However, implementing dynamic pricing successfully requires a deep understanding of its intricacies and a careful evaluation of its suitability for your specific business model. This article explores the core principles of dynamic pricing, delving into its benefits, challenges, and critical considerations to determine if it is the right approach for your e-commerce business.
Are you seeking strategies to bolster your e-commerce profitability and enhance your competitive edge? Dynamic pricing offers a data-driven approach to pricing optimization, moving beyond static pricing models to capitalize on market dynamics. This article provides a comprehensive overview of dynamic pricing strategies, exploring the key factors to consider when implementing this approach. From analyzing market trends and understanding customer behavior to choosing the right software and mitigating potential risks, we’ll examine the essential steps to mastering dynamic pricing and achieving optimal results for your e-commerce business.
What is Dynamic Pricing?
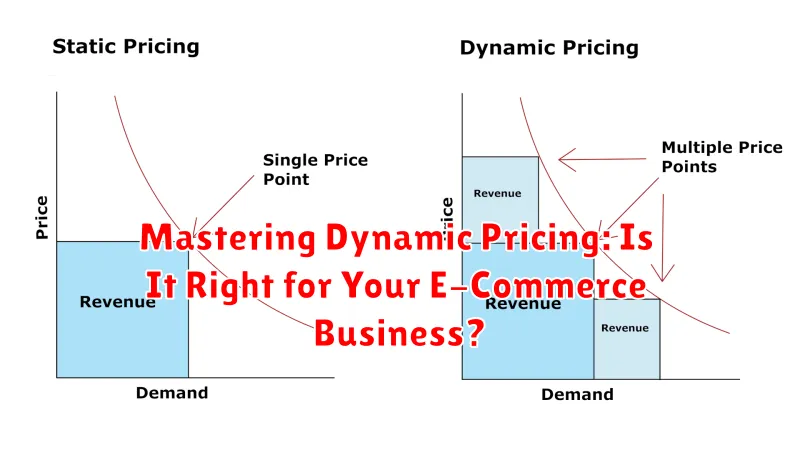
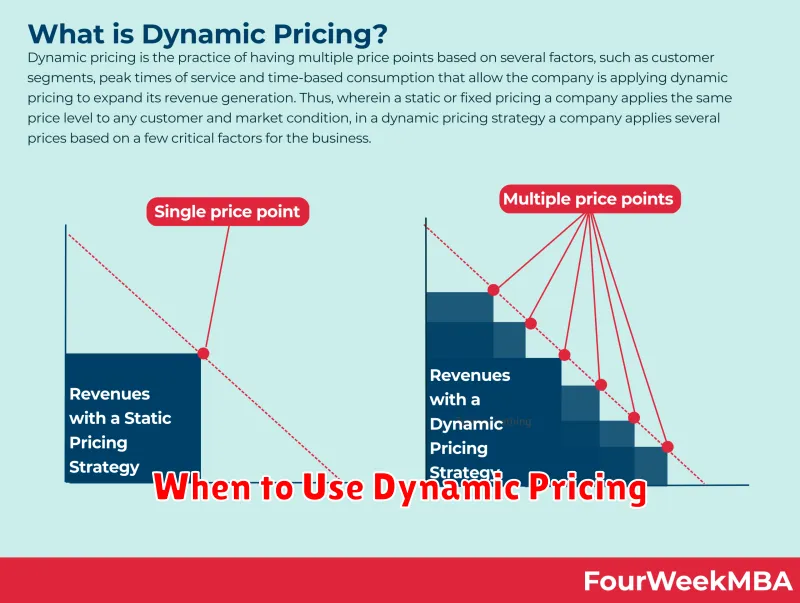
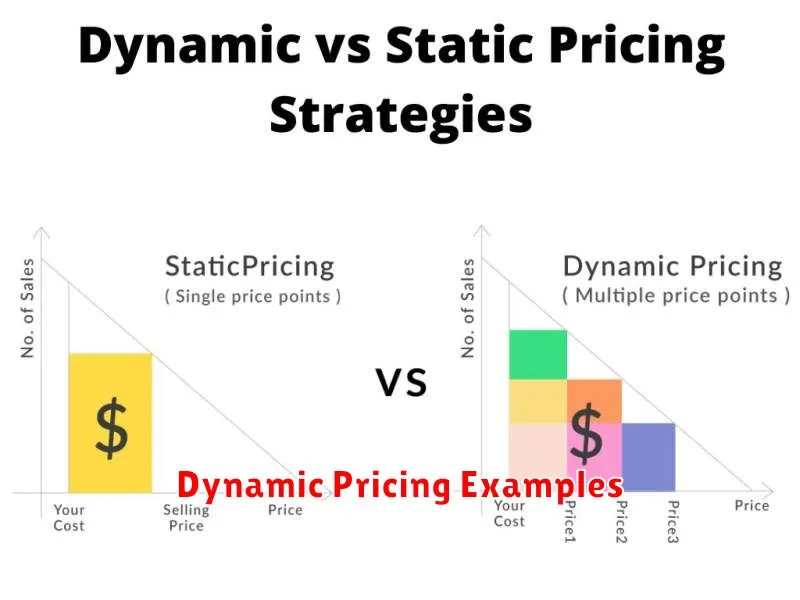
Dynamic pricing, also known as surge pricing, time-based pricing, or demand pricing, is a pricing strategy where businesses set variable prices for products or services that change in response to real-time supply and demand factors. Instead of fixing a single price point, businesses using dynamic pricing adjust prices fluctuating based on algorithms that consider various market conditions.
These conditions can include competitor pricing, seasonality, customer demand, inventory levels, and even time of day. Essentially, dynamic pricing allows businesses to maximize revenue potential by charging more when demand is high and potentially less when demand is low to stimulate sales.
This contrasts with static pricing, where prices remain fixed for a longer duration regardless of market fluctuations.
How Dynamic Pricing Works
Dynamic pricing relies on sophisticated algorithms that analyze a multitude of data points to determine optimal pricing in real-time. These algorithms consider factors such as competitor pricing, demand fluctuations, seasonality, and even time of day.
The process begins by establishing a baseline price. This price serves as an anchor and is often based on cost-plus pricing or value-based pricing. From there, the algorithms adjust the price upwards or downwards based on the real-time data analysis. For example, if demand surges for a particular product due to a competitor running out of stock, the algorithm may increase the price to capitalize on the increased demand. Conversely, if sales are slow, the algorithm might lower the price to stimulate purchases.
Automated repricing software is typically used to implement dynamic pricing. This software integrates with e-commerce platforms and automatically updates prices based on the algorithms’ output. The frequency of price changes can vary, from several times a day to even every few minutes, depending on the specific setup and the volatility of the market.
Advantages of Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing offers several compelling advantages for e-commerce businesses willing to embrace its complexities. One key benefit is increased revenue and profitability. By adjusting prices in real-time to reflect demand, businesses can maximize their earnings potential on each sale.
Another significant advantage is improved competitiveness. Dynamic pricing allows businesses to quickly respond to market changes and competitor pricing strategies, ensuring they remain competitive and attractive to customers. This agility is crucial in today’s fast-paced online marketplace.
Enhanced data-driven insights are also a major benefit. Implementing dynamic pricing often necessitates collecting and analyzing extensive data on customer behavior, market trends, and competitor activity. This data can then be used to inform broader business strategies and optimize other areas of operation.
Finally, dynamic pricing enables greater pricing control and flexibility. Businesses can define pricing rules and parameters to align with their overall business objectives and fine-tune pricing strategies as needed to achieve optimal results.
Disadvantages of Dynamic Pricing
While dynamic pricing offers several benefits, it also presents potential drawbacks that businesses must carefully consider. A primary concern is the risk of alienating customers. Frequently fluctuating prices can erode customer trust and loyalty, particularly if perceived as unfair or manipulative. Price volatility can lead to negative price comparisons with competitors, driving customers away.
Complexity is another disadvantage. Implementing and managing a dynamic pricing strategy requires sophisticated software and a deep understanding of market dynamics. Analyzing large datasets and adjusting pricing algorithms can be resource-intensive and require specialized expertise.
The potential for price wars is also a concern. In highly competitive markets, dynamic pricing can trigger retaliatory price reductions from competitors, leading to a race to the bottom and reduced profit margins for all involved. This can be especially detrimental to smaller businesses lacking the resources to sustain prolonged price competition.
When to Use Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing isn’t a universal solution and its effectiveness depends heavily on the specific circumstances of your business. Consider implementing dynamic pricing when the following conditions are met:
High Sales Volume and Data Availability:
Dynamic pricing algorithms thrive on data. A large volume of sales data is crucial for accurate price adjustments. Without sufficient data, the algorithm may make inaccurate predictions, leading to suboptimal pricing.
Competitive Market:
In highly competitive markets, dynamic pricing can help you stay ahead of the curve. If your products are similar to others available, adjusting prices in real-time allows you to react to competitor price changes and maintain a competitive edge.
Variable Demand and Costs:
If your products experience fluctuations in demand (e.g., seasonal products) or if your input costs change frequently, dynamic pricing can help optimize profitability by adjusting prices to reflect these variations.
Sufficient Margins:
Dynamic pricing involves some degree of price reduction. Ensure your products have sufficient profit margins to accommodate these fluctuations without jeopardizing profitability.
Implementing Dynamic Pricing in Your Business
Implementing dynamic pricing requires a strategic approach. Begin by clearly defining your business objectives. Are you aiming to maximize revenue, increase market share, or clear out inventory? Different objectives will require different pricing strategies.
Next, identify your key pricing variables. These might include competitor pricing, demand fluctuations, seasonality, and even time of day. Data analysis is crucial. Gather historical sales data, market trends, and competitor pricing information. This data will inform your pricing algorithms.
Choosing the right dynamic pricing software is essential. Consider factors such as ease of integration with your existing e-commerce platform, the level of customization offered, and reporting capabilities. Start with a small-scale implementation to test and refine your strategy before a full rollout.
Best Practices for Dynamic Pricing
Implementing dynamic pricing effectively requires careful planning and execution. Establishing clear objectives is paramount. Define what you aim to achieve with dynamic pricing, whether it’s maximizing revenue, increasing market share, or improving profitability.
Data analysis is crucial. Thoroughly analyze historical sales data, competitor pricing, and market trends. This data-driven approach will inform your pricing strategies and prevent uninformed decisions.
Price segmentation allows you to tailor prices to specific customer segments. Consider factors like demographics, purchase history, and location to offer personalized pricing.
Continuous monitoring is essential. Regularly review the performance of your dynamic pricing strategy and make adjustments as needed. Market conditions and customer behavior can change rapidly, so flexibility is key.
Finally, transparency is important, particularly with loyal customers. While you don’t need to disclose every detail of your pricing algorithm, avoid drastic price fluctuations that can erode trust. Communicate clearly any changes in pricing structure to maintain customer relationships.
Dynamic Pricing Examples
Let’s illustrate dynamic pricing with a few examples across different sectors. Imagine an airline adjusting ticket prices based on demand. As seats fill up, especially closer to the departure date, the prices increase. Conversely, if a flight has many empty seats, the airline might lower prices to incentivize bookings.
E-commerce retailers frequently use dynamic pricing. A common example is pricing popular electronics. During high-demand periods like Black Friday, prices may surge due to increased competition and limited stock. Conversely, prices might decrease during slower sales periods.
Ride-sharing services also utilize dynamic pricing. During rush hour or special events, when demand is high and drivers are scarce, prices surge. This incentivizes more drivers to come online and balances supply with demand. Prices typically decrease during periods of lower demand.
Measuring the Success of Dynamic Pricing
After implementing dynamic pricing, continuous monitoring is crucial. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) provide quantifiable metrics to assess its effectiveness.
Track conversion rates. Are customers still purchasing at the adjusted prices? A dip might signal prices are too high. Conversely, a significant increase without a corresponding revenue increase may indicate prices are too low.
Monitor profit margins. This is a core metric. Dynamic pricing should ultimately improve profitability. Calculate the difference between your cost and selling price at the various dynamic price points to ensure healthy margins.
Analyze competitor pricing. Stay informed about their pricing strategies. This helps understand market dynamics and adjust your dynamic pricing rules accordingly.
Gather customer feedback. Surveys and reviews can offer valuable insights into customer perceptions of your pricing. Negative feedback regarding price fluctuations may necessitate adjustments to your strategy.