In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, headless e-commerce has emerged as a transformative approach to online retail. This comprehensive guide will delve into the power of headless e-commerce, exploring its core principles, advantages, and how it can empower businesses to create exceptional customer experiences. Understanding the intricacies of headless commerce is crucial for staying competitive and adapting to the ever-changing demands of the modern consumer. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to unlock the full potential of a headless architecture for your online store, covering key aspects from implementation to optimization.
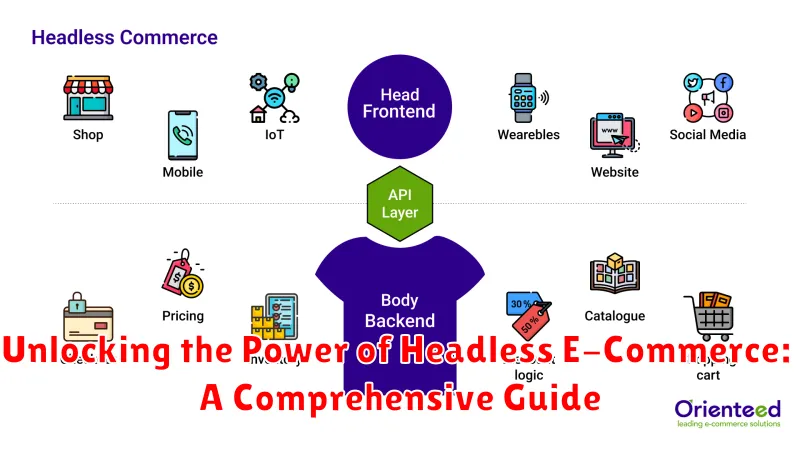
Headless e-commerce decouples the front-end presentation layer (the “head”) from the back-end commerce functionality. This separation offers unprecedented flexibility and scalability, allowing businesses to create highly customized and personalized shopping experiences across multiple touchpoints. Whether you are seeking improved site performance, seamless omnichannel integration, or the ability to rapidly adapt to emerging technologies, headless commerce offers a compelling solution. This guide will provide a detailed overview of headless e-commerce architecture, its benefits compared to traditional platforms, and practical strategies for successful implementation. We will explore how headless solutions can empower your business to deliver truly engaging and innovative customer journeys.
Understanding the Core Concepts of Headless E-Commerce
Traditional e-commerce platforms tightly couple the frontend (customer-facing interface) and the backend (business logic and data). Headless e-commerce, in contrast, decouples these two components. This separation allows businesses to use any frontend technology they choose while leveraging the power of a robust e-commerce backend.
The core concept revolves around an API (Application Programming Interface). This API acts as a bridge, enabling communication and data exchange between the frontend and backend. The frontend sends requests to the backend via the API, receiving product information, customer data, and other necessary resources. This allows for greater flexibility and customization.
The backend continues to manage all essential e-commerce functionalities, such as inventory management, order processing, and payment gateways. Meanwhile, the frontend can be a website, mobile app, or any other digital touchpoint. This decoupled architecture empowers businesses to deliver seamless and personalized experiences across various channels.
How Headless E-Commerce Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
Headless e-commerce separates the frontend presentation layer (the “head”) from the backend commerce functionality. This decoupling allows for greater flexibility and customization.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Customer Interaction: A customer interacts with the frontend interface (website, mobile app, IoT device, etc.).
- API Request: The frontend sends a request to the backend commerce platform via an API (Application Programming Interface).
- Data Retrieval: The backend processes the request and retrieves the necessary data (product information, inventory, pricing, etc.).
- Response Delivery: The backend delivers the requested data back to the frontend via the API in a structured format (e.g., JSON).
- Content Presentation: The frontend receives the data and dynamically renders it to the customer in the desired presentation format.
This API-driven approach enables businesses to deliver consistent and personalized commerce experiences across various touchpoints without being constrained by the limitations of a traditional monolithic platform.
Benefits of Adopting a Headless E-Commerce Architecture

Headless e-commerce offers a range of advantages for businesses looking to enhance their online presence and customer experience. A key benefit is increased flexibility. Decoupling the frontend and backend allows for faster and more agile development, enabling businesses to quickly adapt to changing market trends and customer demands.
Improved performance is another compelling advantage. By optimizing the frontend independently, businesses can achieve significantly faster page load speeds, resulting in a better user experience and higher conversion rates. This separation also allows for seamless integrations with various third-party services, such as CRM, ERP, and marketing automation platforms, streamlining business operations.
Furthermore, headless e-commerce empowers businesses to deliver omnichannel experiences. With a headless architecture, businesses can easily distribute content and product information across multiple touchpoints, including websites, mobile apps, social media platforms, and IoT devices, creating a consistent and unified brand experience for customers.
Exploring the Different Types of Headless E-Commerce Platforms
Several types of headless e-commerce platforms cater to different business needs and technical capabilities. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the optimal solution.
1. API-First Platforms
These platforms are built with APIs as the core foundation, enabling seamless integration with various front-end systems and third-party services. They offer great flexibility and scalability for complex e-commerce operations.
2. SaaS-Based Platforms
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms provide a hosted solution with pre-built functionalities and APIs for headless operations. They are generally easier to implement and manage, requiring less technical expertise compared to self-hosted options.
3. Open-Source Platforms
Open-source solutions provide greater control and customization options, as businesses have access to the source code. However, they typically demand more technical resources for setup, maintenance, and ongoing development.
4. Hybrid Platforms
Some platforms offer a hybrid approach, combining features of both traditional and headless architectures. This can be a viable option for businesses transitioning to headless gradually or requiring specific legacy integrations.
Choosing the Right Headless E-Commerce Solution for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate headless e-commerce solution requires careful consideration of your business’s specific needs and goals. Several key factors will influence your decision.
First, evaluate your scalability requirements. Will your platform need to handle rapid growth in traffic and transactions? Some solutions are better equipped for scaling than others.
Next, consider your integration needs. Think about your existing systems, such as CRM, ERP, and marketing automation platforms. Ensure the headless solution offers seamless integration capabilities.
Budget is another critical factor. Headless solutions range in price, so determine your budget and explore options within that range.
Finally, assess the technical expertise within your team. Some platforms require more technical knowledge than others. Choosing a solution that aligns with your team’s capabilities is crucial for successful implementation.
Integrating Headless E-Commerce with Your Existing Systems
Integrating a headless e-commerce solution with your existing systems requires careful planning and execution. A key aspect is choosing the right integration points. Common integration points include CRM (Customer Relationship Management), ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), CMS (Content Management System), and marketing automation platforms. Connecting these systems allows for seamless data flow and enhanced business operations.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) play a crucial role in facilitating this integration. A robust API allows your existing systems to communicate with the headless e-commerce platform, exchanging data such as product information, customer data, and order details. This allows for a unified view of your business operations and facilitates personalized customer experiences.
Consider the data flow between systems. Determine which data needs to be exchanged, the frequency of updates, and the format of the data. Properly mapping data fields ensures consistency and prevents errors. Additionally, consider the security implications of connecting your systems and implement necessary security measures.
Real-World Examples of Successful Headless E-Commerce Implementations
Several companies across diverse industries have leveraged headless e-commerce to achieve significant business improvements. These examples showcase the versatility and adaptability of this approach.
Example 1: Fashion Retailer Improves Mobile Experience
A prominent fashion retailer adopted a headless architecture to enhance their mobile shopping experience. By decoupling the frontend from the backend, they were able to create a fast, responsive mobile interface optimized for browsing and purchasing on smaller screens, resulting in increased mobile conversions.
Example 2: Food Delivery Service Streamlines Ordering
An online food delivery service implemented a headless CMS to manage their vast menu and ordering system more efficiently. This allowed them to quickly update menu items, pricing, and promotions across multiple platforms and devices, streamlining their operations and improving customer satisfaction.
Example 3: B2B Company Personalizes Customer Portals
A B2B company utilized a headless platform to create personalized customer portals. This offered tailored product catalogs, pricing, and order history, strengthening customer relationships and driving repeat business.
Future Trends in Headless E-Commerce Development
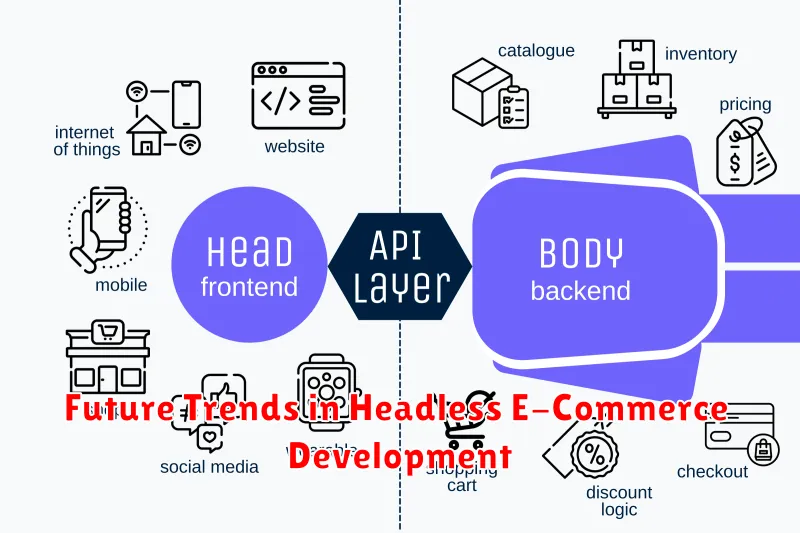
The future of headless e-commerce is brimming with exciting possibilities. Artificial Intelligence (AI) will play a larger role, enabling personalized product recommendations and dynamic pricing strategies. Expect to see more sophisticated AI-powered chatbots providing enhanced customer service.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technologies are poised to revolutionize the online shopping experience. Customers will be able to visualize products in their own environment or even “try on” clothes virtually before purchasing. This immersive experience will bridge the gap between online and brick-and-mortar shopping.
The growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) will open up new channels for commerce. Connected devices, from smart refrigerators to voice assistants, will facilitate seamless purchasing experiences, allowing customers to replenish household items or make purchases with simple voice commands.
Finally, Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) will continue to gain traction, offering enhanced speed and offline functionality. These apps provide a more native-like experience on mobile devices, leading to increased customer engagement and conversion rates.